
Computing

ACM Transactions on Graphics 37(4) (SIGGRAPH 2018)
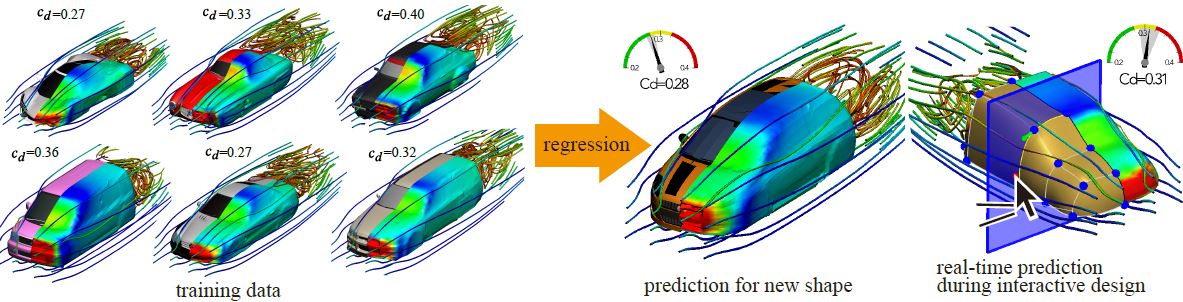
We present a data-driven technique to instantly predict how fluid flows around various three-dimensional objects. Such simulation is useful for computational fabrication and engineering, but is usually computationally expensive since it requires solving the Navier-Stokes equation for many time steps. To accelerate the process, we propose a machine learning framework which predicts aerodynamic forces and velocity and pressure fields given a threedimensional shape input. Handling detailed free-form three-dimensional shapes in a data-driven framework is challenging because machine learning approaches usually require a consistent parametrization of input and output. We present a novel PolyCube maps-based parametrization that can be computed for three-dimensional shapes at interactive rates. This allows us to efficiently learn the nonlinear response of the flow using a Gaussian process regression. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach for the interactive design and optimization of a car body.
@article{Umetani:2018,
author = {Umetani, Nobuyuki and Bickel, Bernd},
title = {Learning Three-dimensional Flow for Interactive Aerodynamic Design},
journal = {ACM Transactions on Graphics (SIGGRAPH 2018)},
year = {2018},
volume = {37},
number = {4},
articleno = {89},
numpages = {10},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3197517.3201325},
doi = {10.1145/3197517.3201325},
publisher = {ACM},
address = {New York, NY, USA}
}
We thank anonymous reviewers and Ryan Schmidt for their comments and advice. We appreciate the assistance from Rin Ishikawa for the production of the supplemental video. This project has received funding from the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (grant agreement No 715767 – MATERIALIZABLE).

