
Computing

ACM Transactions on Graphics (Siggraph Asia 2023)
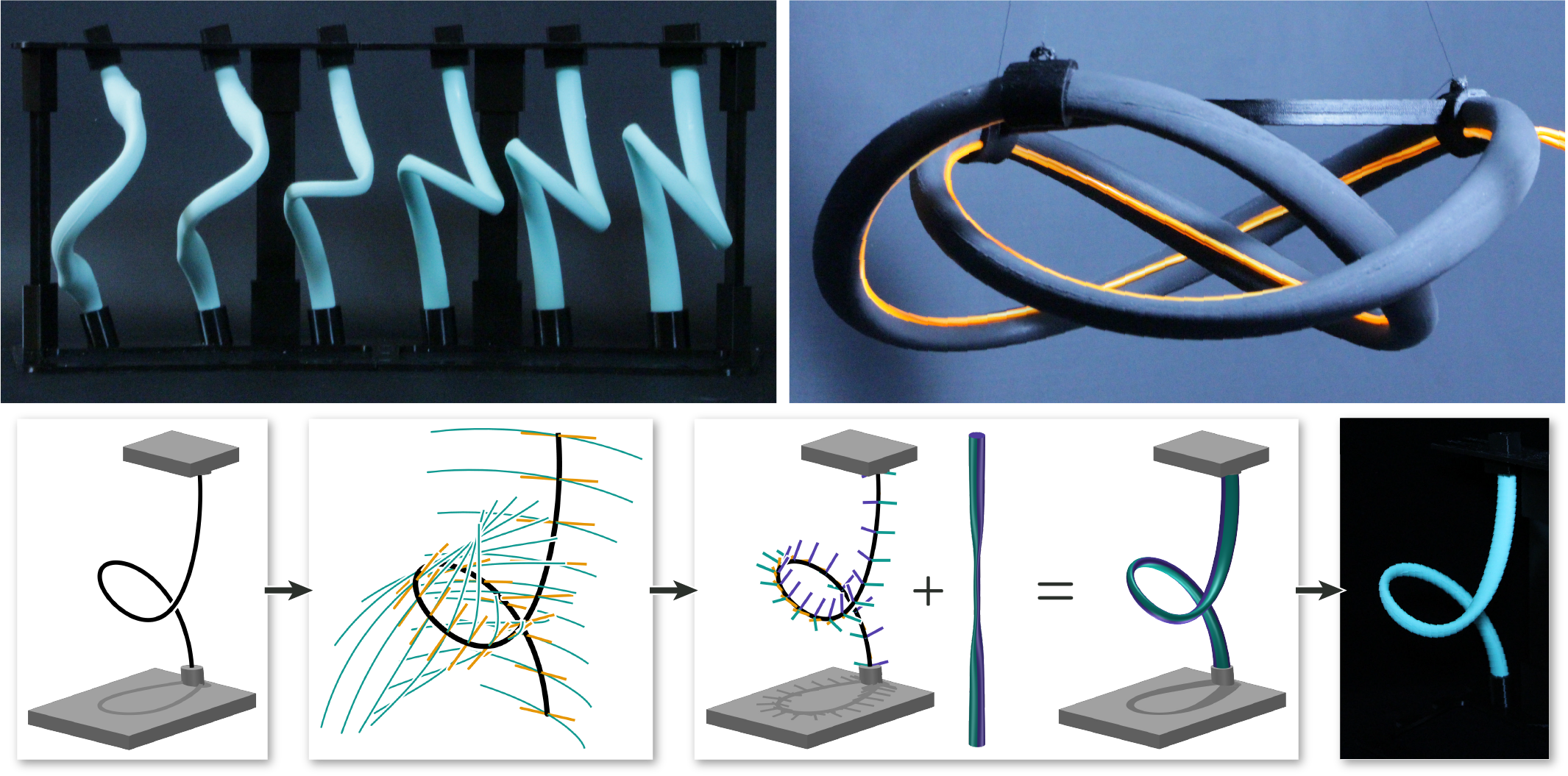
The Kirchhoff rod model describes the bending and twisting of slender elastic rods in three dimensions, and has been widely studied to enable the prediction of how a rod will deform, given its geometry and boundary conditions. In this work, we study a number of inverse problems with the goal of computing the geometry of a straight rod that will automatically deform to match a curved target shape after attaching its endpoints to a support structure. Our solution lets us finely control the static equilibrium state of a rod by varying the cross-sectional profiles along its length. We also show that the set of physically realizable equilibrium states admits a concise geometric description in terms of linear line complexes, which leads to very efficient computational design algorithms. Implemented in an interactive software tool, they allow us to convert three-dimensional hand-drawn spline curves to elastic rods, and give feedback about the feasibility and practicality of a design in real time. We demonstrate the efficacy of our method by designing and manufacturing several physical prototypes with applications to interior design and soft robotics.
@article{KirchhoffHafner23,
author = {Hafner, Christian and Bickel, Bernd},
title = {The Design Space of Kirchhoff Rods},
year = {2023},
issue_date = {October 2023},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
volume = {42},
number = {5},
issn = {0730-0301},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3606033},
doi = {10.1145/3606033},
journal = {ACM Trans. Graph.},
month = {sep},
articleno = {171},
numpages = {20},
keywords = {Kirchhoff Rods, Digital Fabrication, Active Bending, Computational Design}
}
We thank the anonymous reviewers for their generous feedback, and Julian Fischer for his help in proving Proposition 1. This project has received funding from the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (grant agreement No. 715767).

